What is Cyber Security?
Cyber security is a term that gets banded around a lot but its meaning can often be hard to pin down, as it encompasses a wide range of defensive measures, procedures and systems. In this guide, we’re going to take an in-depth look at what cyber security is, why it’s important and the different categorisations of cyber security and cyber attacks. I’ll end by taking a brief look at some of the cyber security courses available to those looking to get into or further their career in cyber security.

What are the Different Types of Cyber Security?
The term ‘cyber security’ refers to the group of defensive measures, processes and technologies that protect individual computers and networks and with the information and programs on them. Various tactics can be employed by organisations and businesses in order to protect these systems and the data stored on them. Individuals can also take responsibility of their own data by constantly updating their anti-virus software and becoming web savvy in order to avoid phishing scams and other forms of social engineering.
Broadly speaking, cyber security can be broken down into five key areas and these are as follows:
Application Security
The protection of applications from outside threats is one of the most important aspects of cyber security. With so many applications now accessing the internet, it has become important to protect application security through countermeasures like application firewalls that curtail the access of data by installed programs. Other countermeasures include hiding IP addresses from the internet through a router, encryption, anti-virus software and biometric and password security systems.
Network Security
Networks are fundamental to the IT infrastructure of most modern businesses. Network security includes access control which protects allows genuine users to be recognised by the network, keeping out outside attackers. Network segmentation allows network traffic to be classified, which makes the enforcement of network security policy far easier and manageable. Network security officers and engineers are responsible for designing and implementing security measures and policies to protect the business network. Having a secure network is one of the most important parts of IT management and you should ensure you choose an excellent IT support provider that has Cyber Essentials or higher, showing they take network security seriously.
Information Security
Often abbreviated to InfoSec, information security refers to the strategies that are put in place to maintain the triad of information confidentiality, integrity and availability (the CIA triad). InfoSec will often mean finding a balance between these three requirements that balances the threats identified by risk assessments and the need for continuing business operation. As with application and network security, appropriate countermeasures will be implemented based off the constant assessment of risks and vulnerabilities.
Operational Security
Operational security is an analytical process that was originally developed by the military. It seeks to identify critical information, determine who or what the potential threats and what vulnerabilities they could exploit. A thorough risk assessment is then used to determine the level of each threat and what countermeasures to employ. Unlike InfoSec, operational security seeks to understand an organisation’s cyber security practices from the outside in by putting itself in the shoes of a potential hacker.
Education and Best Practice
One of the least talked about but most important aspects of cyber security is the ongoing education of end users and the development of best practice. It’s often said that the weakest link in any cyber security system are the human beings that rely on it. By educating non-technical workers organisations can avoid the chance of silly mistakes happening, such as employees opening potentially harmful emails or introducing unchecked bootable media to a company computer.
What are the Motivations behind Cyber Attacks?
As our world has become increasingly interconnected and dependent on technology, cybercrime has evolved and grown with it. In many ways cybercrime is an evolution of existing criminal activity, whether it be directed by states or gangsters. As we have put more everyday information, systems and processes online, the motivation for illicitly accessing, altering or destroying them become stronger.
The criminal motives behind cyber attacks are often financially motivated but this is not always the case. Agendas can range from ideological conviction to simple boredom or showboating and actors carrying out these crimes can be anything from disaffected teenagers to terrorist organisations and high tech national security services.
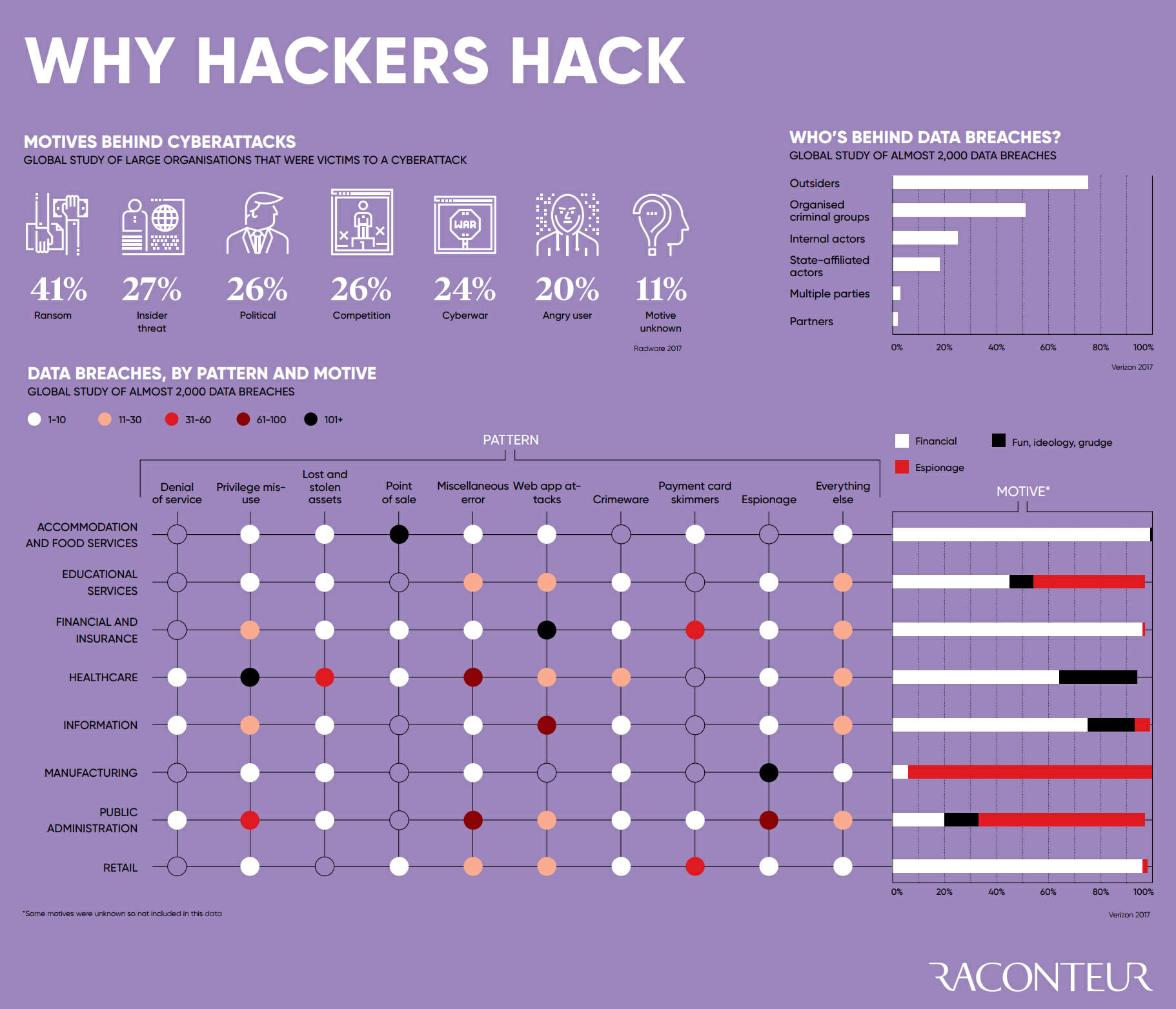
Broadly speaking then, cyber threats can be broken down into one of three distinctive types of attack.
- Attacks on target’s confidentiality: These are attacks characterised by stealing or copying confidential information in order to gain access to a personal account or system in order to commit fraud or extort money or influence through blackmail.
- Attacks on target’s availability: Attacks on availability are all about preventing a target from accessing their own data or systems. Two typical types of availability attack are ransomware and distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks.
- Attacks on target’s integrity: Attacks on integrity are less about access or preventing access to data or systems and more about corrupting, destroying or damaging those systems. These attacks are sabotage and are often politically or ideologically motivated.
Each of these three types of attack has its own distinctive purpose that presupposes the use of specific methods or techniques in order to achieve and it’s these I now want to look at.
Common Cyber Security Vulnerabilities and Attacks
Let’s look at some of the most common methods of cyber attack before we go onto look at how cyber security measures can prevent or mitigate against them.
Backdoor Vulnerabilities
A backdoor is a vulnerability in any system that can be exploited in order for a user to gain access, bypassing normal authentication controls. A backdoor can exist by design or by accident (due to poor configuration or oversight in development) but once discovered they expose any system to those who are aware of it and capable of exploiting it.
Denial of Service Attacks (DoS)
A typical type of attack on availability, a denial of service attack seeks to cripple a system (usually a server upon which a service or website relies) by overloading it with requests. This is relatively easy to defend against by blocking the offending IP address through a firewall. A distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack however is harder to defend against as it employs multiple ‘zombie machines’ (sometimes called a botnet) in order to flood a server with requests.
Direct Access Attacks
A direct access attack is exactly as the name suggests and involves gaining physical access to a computer in order to tamper with it, steal information directly from it or install malware like a keylogger or listening device. Access even to a password protected system may be possible through a CD-ROM booted tool or installation of another operating system.
Malware
Malware is a portmanteau of ‘malicious software’ and refers to any program that is harmful to a user’s computer or network. There are various forms of malware and they can be surreptitiously installed in a number of ways, including phishing emails redirecting user’s to fake websites, corrupted USB sticks and hacking a system via a backdoor. Malware comes in a number of forms including worms, viruses, spyware, Trojan Horses and ransomware.
Social Engineering
Social engineering is really not that different from the con tricks of old and is one of least technical means of gaining access to passwords and as a result personal or sensitive information. Often this will be bank accounts but in the case of a small business it may be access to a network or remote desktop.
Why is Cyber Security Important?
It’s safe to say that cybercrime is something that worries a lot of us. It’s also safe to say that a lot of us don’t know what to do about it and probably don’t take the simple precautions we should do to avoid becoming a victim of it.
Let’s leave aside the huge amount of sensitive and potentially vulnerable data we all store on our own personal internet connected devices for a minute though and look solely at how cybercrime affects UK businesses.
In 2017 the UK Government’s Cyber Security Breaches Survey found the average cost of a security breach to be £19,600 for a large company and £1570 for a small business. 74% of businesses surveyed said cyber security is now a high or very high priority for their business. Of those surveyed, 46% said they had been the victim of a breach in the last year with that figure rising to two thirds for medium and large sized businesses.
It’s not difficult to see from these figures why cyber security is important to businesses. The cost of cyber security breaches is often manageable but often they are enough to bring down an established business or erode consumer confidence in it enough to see it go under in the months or years preceding a major breach.
There is also the , which affects all businesses within the EU or trading with the EU. The consequences of this are far reaching and I want to look at this in more detail in a future blog post.
Training and Certification in Cyber Security
There are many ways to get into the cyber security industry. Landing your first junior IT security job will require having the right experience and the right qualifications. Some of the most popular courses available in the UK include:
- Bachelor’s degree in Cyber Security and/or Forensic Computing
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Certificate in Information Security Management Principles (CISMP)
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
- CompTIA Security+
- CompTIA Network+
- ISO27001 Foundation
- ISO27001 Lead Implementer courses
The cyber security industry is a rapidly growing one and faces a looming recruitment crisis so there’s never been a better time to start training in IT security. There are a huge number of training courses and qualifications out there but knowing where to start can be daunting. The Cyber Security Courses homepage has plenty of good advice and we’ll be publishing a steady stream of great in-depth advice and guides on the blog there and here.
Research and Sources:
- http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/cybersecurity
- https://www.csoonline.com/article/3242690/data-protection/what-is-cyber-security-how-to-build-a-cyber-security-strategy.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer_security
- https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/security/what-is-cybersecurity.html
- https://www.business2community.com/cybersecurity/great-security-jobs-crisis-01999077

